Virtual Physics Experiments: Learn Everything About Digital Experiments
Physics is a fascinating subject that deals with nature’s basic laws. One of the best ways to learn physics is by doing experiments. Traditionally, students performed these experiments in a physical laboratory setting. This is where virtual physics experiments come in. Virtual physics experiments are computer simulations of real-world physics experiments.
In this blog, we will explore the world of virtual physics experiments. We will also delve into the benefits of using advanced digital physics simulations in the learning process.
Challenges and problems faced by students in physics laboratory
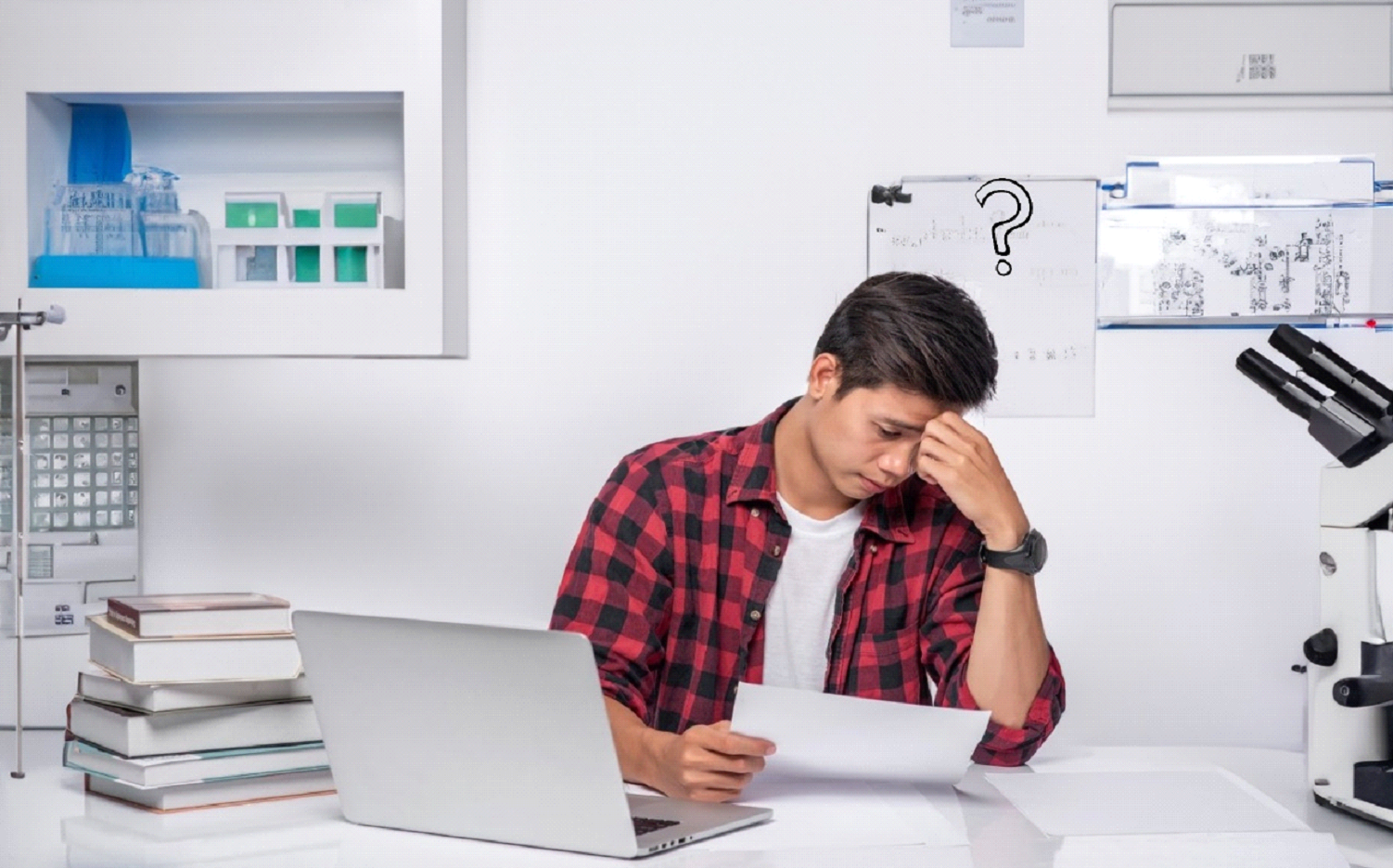

Before delving into virtual experiments, it is essential to understand the challenges that students often face in physical physics laboratories:
- Limited Equipment Availability: Many schools and colleges have limited resources, resulting in inadequate equipment for conducting experiments. This scarcity often forces students to share equipment, limiting their hands-on experience.
- Time Constraints: Physical labs often have strict time constraints. Students may have only a limited time to complete experiments, which can lead to rushed or incomplete observations.
- Safety Concerns: Physics experiments can involve dangerous elements, such as high voltages or chemicals. Ensuring the safety of students in a physical lab is a constant concern for instructors.
- Inadequate Supervision: In a crowded lab with limited instructors, it is challenging for each student to receive personalized guidance and supervision. This can hinder their understanding and ability to perform experiments correctly.
- Equipment Malfunction: Mechanical and electrical equipment can malfunction, disrupting experiments and causing frustration for students.
- Resource Constraints: Many schools struggle to maintain and upgrade their lab equipment due to budget constraints, leading to outdated or non-functional apparatus.
Benefits of advanced digital physics simulations
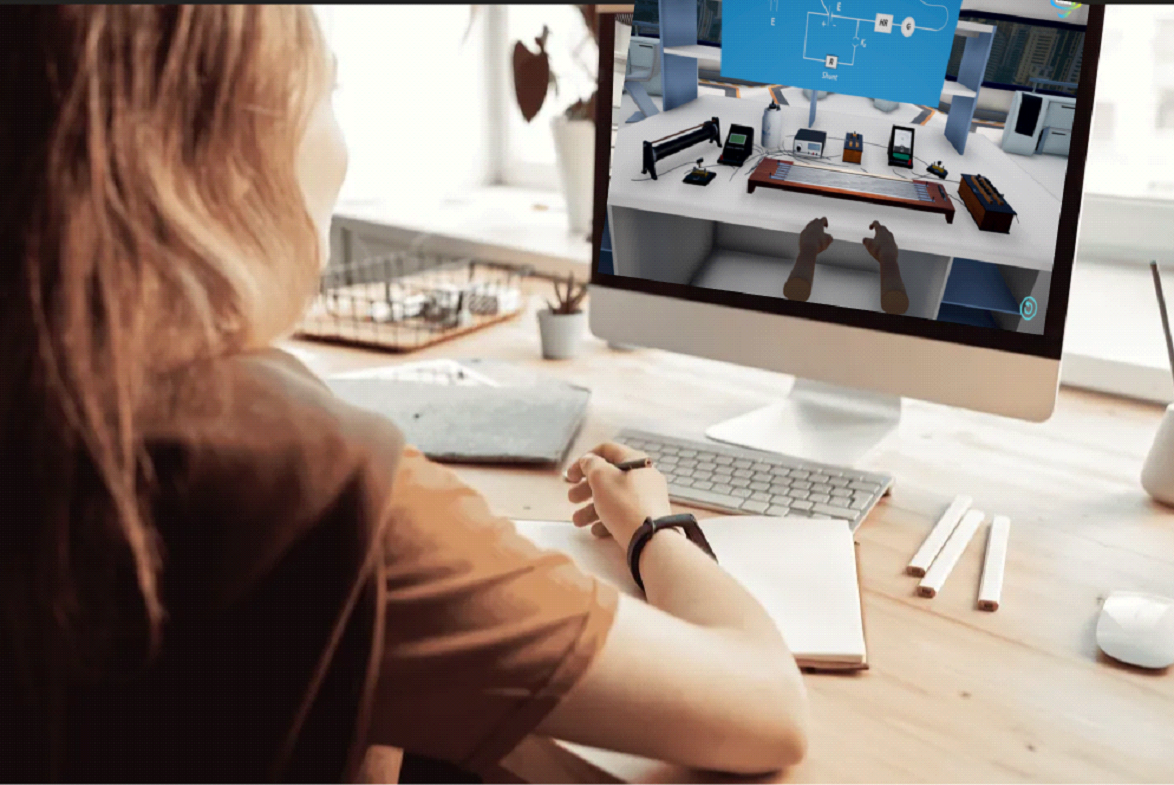

Now, let’s explore how advanced digital physics simulations address these challenges while offering numerous benefits:
- Accessibility: Virtual experiments eliminate the constraints of physical laboratories, making them accessible to students regardless of their geographical location. This is especially beneficial for students in remote areas or those with limited access to laboratory facilities.
- Safety: Dangerous experiments involving high voltages or hazardous materials can be simulated safely in a digital environment, reducing the risk to students and instructors.
- Unlimited Resources: Virtual simulations provide an almost limitless array of resources and equipment, allowing students to perform experiments with various parameters and conditions, enhancing their understanding of underlying concepts.
- Instant Feedback: In virtual experiments, students receive immediate feedback, enabling them to rectify mistakes and gain a deeper understanding of the experimental process.
- Cost-Efficiency: Setting up and maintaining a physical laboratory can be expensive. Virtual experiments reduce costs associated with equipment, maintenance, and consumables.
- Time Efficiency: Digital simulations save valuable class time that would otherwise be spent setting up and conducting experiments, allowing educators to cover more content.
- Enhanced Visualization: Virtual experiments often come with advanced graphics and animations, making it easier for students to visualize complex physical phenomena.
- Customization: Students can repeat experiments multiple times with different parameters, reinforcing their learning and experimentation skills.
How are these virtual physics experiments developed?
Ever wondered how these experiments are created? Creating digital and virtual physics experiments involves the application of various scientific principles and technologies to simulate physical phenomena and interactions in a computerized environment. Let’s know the science and development process behind digital and virtual physics experiments.
- Understanding the Physics: Developers must have a deep understanding of the physics principles they want to simulate.
- Mathematical Modelling: Physics simulations often begin with mathematical models that describe the behaviour of physical systems. These models use equations, such as Newton’s laws of motion or Maxwell’s equations for electromagnetism, to represent the underlying physics.
- Programming Languages: Virtual physics experiments are implemented through computer programming using languages like C++, Python, or Java. These languages are chosen based on factors such as efficiency, platform compatibility, and ease of development.
- Simulation Engines: Developers often use specialized simulation engines or libraries that provide tools and functions for modelling and solving physics problems efficiently. Examples include Unity for game-based simulations and libraries like OpenFOAM for fluid dynamics simulations.
- Visualization
- Rendering and Graphics: The visual representation of the virtual experiment is crucial. Developers use computer graphics techniques to render 2D or 3D simulations, including the use of shaders, textures, and lighting to create realistic visuals.
- User Interface (UI): A user-friendly interface is designed to allow users to interact with and control the simulation. This includes features like menus, buttons, sliders, and data visualization tools.
- User Input: Users interact with virtual physics experiments through input devices like a keyboard, mouse, or touchscreen. These inputs are translated into actions within the simulation, such as applying forces, changing parameters, or adjusting settings.
- Real-Time Computation: Physics simulations must run in real-time, providing instantaneous feedback to users as they interact with the virtual experiment. Achieving real-time performance often requires optimizing code and using parallel computing techniques.
- Accessibility and Educational Goals: Digital and virtual physics experiments are often developed with specific educational goals in mind. Developers must consider the target audience and design experiments that align with educational objectives
- Integration with Hardware: In some cases, virtual physics experiments can be integrated with hardware devices like sensors, haptic feedback devices, or virtual reality (VR) headsets to enhance the user experience and provide more realistic interactions.
Experiments in the physics curriculum
Different state boards mandate a set of physics experiments for students. These experiments cover a wide range of topics, including mechanics, electricity, optics, and modern physics. There are many different virtual physics experiments available online. With virtual physics experiments, students can now access a vast repository of experiments that closely mimic real-world scenarios. Some of the most well-known are:
- Simple Pendulum Experiment: This experiment allows students to study the period and frequency of a simple pendulum.
- Ohm’s Law Experiment: By virtually connecting resistors, ammeters, and voltmeters, students can explore Ohm’s law and understand the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance.
- Focal Length of Concave and Convex Mirror: Digital simulations allow students to adjust the object’s position and observe the corresponding image formed by the mirror, helping them understand the concepts of focal length and mirror behaviour.
- Characteristics of a PN Junction Diode: Virtual experiments allow students to alter diode properties by adjusting the voltage and monitoring how it affects the flow of current, which aids in the understanding of semiconductor physics.
These are just a few examples of the many virtual physics experiments that are available. One of the most effective virtual science labs available in the market is SimuLab.
The most effective virtual experiment simulations and virtual lab – SimuLab
SimuLab is a 3D virtual scientific laboratory that enables students to study and conduct experiments – anytime, anywhere. It has the most advanced simulations of K-12 science subjects. SimuLab is an excellent tool for anyone who wants to experience real experiments or learn more about science. It is a cutting-edge learning tool created by IITians using modern technologies such as AI, AR, and VR.
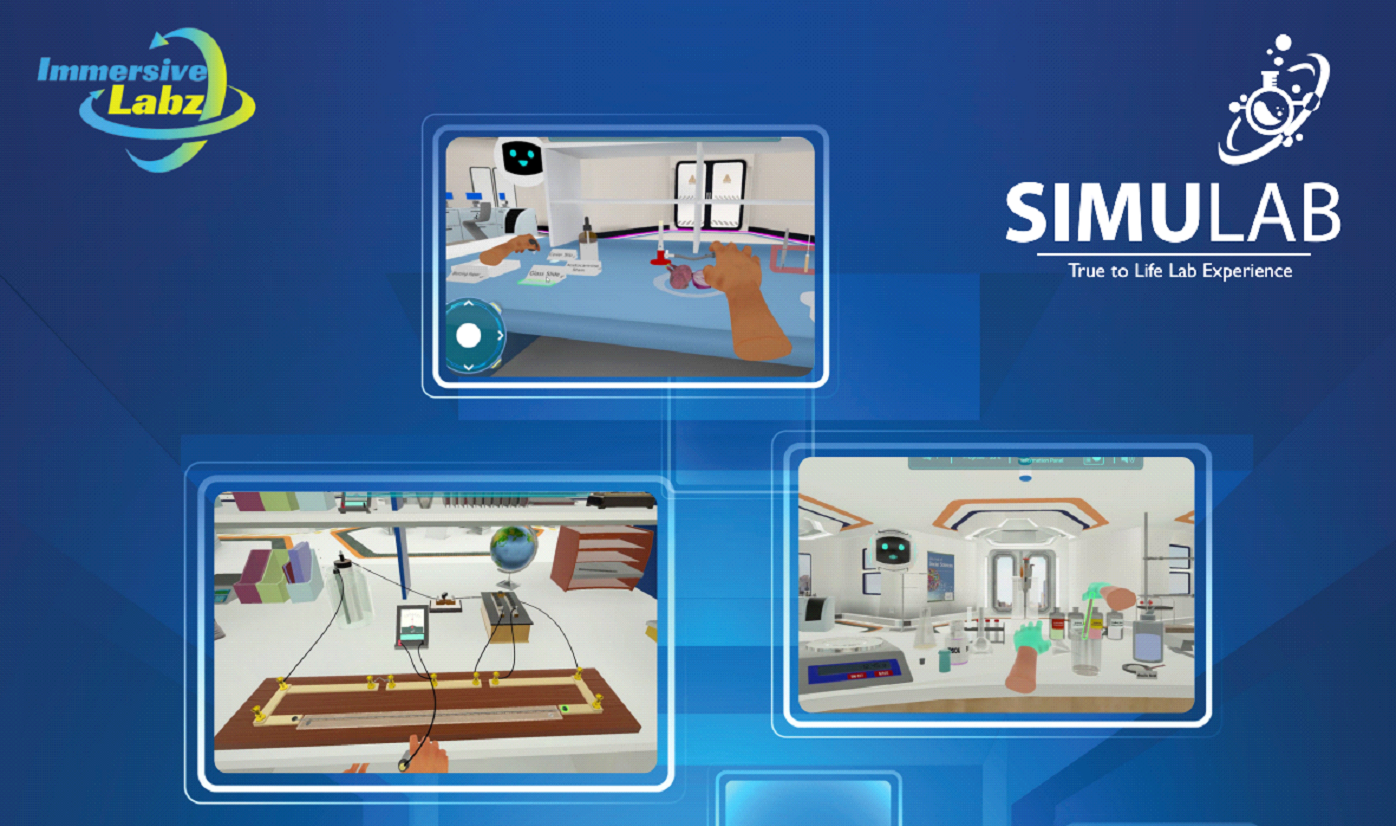

Overview:
- Easily access the science laboratory with convenience and without any difficulties.
- Acquire a simplified and engaging method to learn scientific experiments.
- Receive comprehensive, step-by-step instructions for conducting experiments.
- Foster the development of scientific reasoning and a strong conceptual grasp of the subject.
- Practice experiments an unlimited number of times.
- Retain a deep understanding of scientific concepts over an extended period.
- Achieve improved academic performance and excel in competitive exams such as IIT/NEET.
- Access the platform effortlessly across various devices, including smartphone, desktop, and tablet.
About virtual simulations:
Abundant resources are available to facilitate a comprehensive understanding of each science experiment.
- Aim: Establishes a clear focus on the experiment’s purpose and objectives.
- Objective: Outlines what will be taught, how it will be learned, and what outcomes can be expected from the experiment.
- Safety Precautions: Provides safety guidelines specific to each experiment to ensure a secure laboratory environment.
- Theory: Offers simplified theoretical explanations to aid learners in grasping fundamental concepts.
- Story: Incorporates real-life scenarios related to the subject to enhance engagement in the learning process.
- Simulation: Grants access to an advanced virtual platform for conducting science experiments.
- Quizzes: Includes multiple quiz questions to facilitate better preparation for competitive exams like IIT/NEET.
- Analytics: Allows users to assess their progress and monitor overall progress using a performance dashboard.

Final words
Virtual physics experiments have transformed the way students learn and understand physics concepts. For students, these simulations offer a comprehensive and efficient way to conduct experiments while addressing the challenges faced in physical laboratories. Embracing virtual physics experiments not only keeps students engaged but also prepares them for a world where technology plays an ever-increasing role in scientific research and experimentation.






