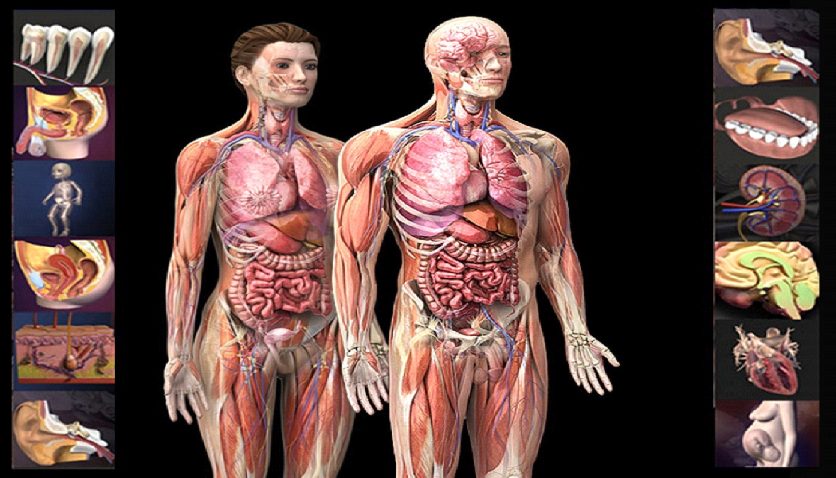
Teaching in medical education is important, intricate, and multi-dimensional. It’s crucial to offer practical anatomy classes so students can practice in clinical settings. Medical students are taught the anatomical structures on human cadavers. Additionally, two-dimensional (2D) anatomy books and images, both in print and digital form, are also used.
Understanding the human body is essential for all health care practitioners, and knowing anatomy is an important step in that process. The use of technology in anatomy teaching has sparked a significant part of the study to determine the advantages of various advances. This blog intends to investigate various learning approaches for 3D human anatomy visualization.
Creative learning methods: Need of the hour!
The majority of medical institutes have decreased the overall number of hours allotted for anatomy instruction and laboratory practicals as a result of the adoption of revised curricula in medical, dentistry, and other allied health schools. To ensure that students understand anatomy as much as possible in the new environment, developing creative teaching and learning methods is the need of the hour.
In the study of anatomy, spatial visualization is important. Not just anatomical features and functions but also spatial links to neighbouring structures must be taught to students. The two-dimensional (2D) static anatomical images used in anatomy textbooks and atlases are useful, but they are not very effective at revealing anatomical systems’ three-dimensional (3D) dynamics.
Challenges in learning with 2D visualizations!
It could be challenging for medical students to understand some dynamic features of functional anatomy and to visualize 2D pictures as 3D. Additionally, because of anatomy’s complexity, medical students and clinicians in training have trouble identifying anatomy in a clinical situation.
Many undergraduate and graduate students evaluate their anatomical knowledge as inadequate despite the variety of instructional techniques available. As compared to conventional approaches, the usage of a 3D tool produced greater levels of factual anatomy knowledge and spatial anatomy knowledge.
Learning Advancement in Anatomy: 3D Human Visualization!
Students can improve their understanding of human anatomy through the use of cutting-edge technology and 3D pictures. There are various ways to study anatomy, including a variety of websites and apps for mobile devices, lectures, oral presentations, 2D graphics (atlases), and cadaver dissection. Dissection of cadavers is frequently regarded as the ideal method for learning anatomy.
Limitations of cadaver dissection:
- Scarcity of cadavers
- Exorbitant expense of acquiring and preserving them
- Ethical controversy surrounding their usage
Considering the above factors, more 3D visualization approaches like virtual cadaver dissection tools are being created nowadays for teaching anatomy.
One such virtual cadaver dissection system recommended by medical professionals is CADAVIZ – India’s first and most advanced virtual human dissection table. It enables students to study anatomy in an immersive way, exploring the minute anatomical details of the human body.

Why 3D human visualization in anatomy education?
- Enhanced understanding: 3D visualization provides a more realistic representation of the human body, making it easier for learners to comprehend complex anatomical structures and their spatial relationships.
- Interactive learning: Learners can actively engage with the 3D models, which promotes better retention and understanding compared to passive learning methods.
- Personalized learning: Students can explore the 3D models at their own pace, enabling personalized learning experiences based on their individual needs and preferences.
- Simulating real-life scenarios: 3D visualization can be used to simulate medical scenarios, surgeries, or clinical cases, allowing learners to apply their knowledge in practical situations.
- Cross-disciplinary applications: 3D human visualization can benefit various fields, including medical education, biology, physical therapy, and other healthcare-related professions.
Final words!
In conclusion, computer-based, virtual reality, and augmented reality 3D learning approaches are generally more successful than conventional ways of teaching anatomy. Overall, 3D Human Visualization has the potential to revolutionize how anatomy is taught and learned, providing a more immersive and comprehensive educational experience for students and medical professionals alike.
Writer – Sneha Adsule
Team Lead Subject Matter Expert-Biology